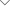- MTE VALUE
- MTE PRODUCTS
>Superior products >Standard catalogue of products >Non-standard customization >Industry Solutions
- MTE INTRODUCE
Industry Solutions
Contact UsTEL:0512-66168600
TEL:0512-66168602
Phone:18913132887Industry Solutions
Locking Reasons and Solutions of Stainless Steel Fasteners
I. Reasons for Locking Stainless Steel Fasteners
1、The deflection angle of thread matching and the softer property of stainless steel are easy to cause locking.
1.1The fit between screw and nut belongs to clearance fit and has the international standard tolerance range of their respective execution. Therefore, the central axis of the external thread is basically not on the same line when matching, because the inclination reduces the contact surface between the internal and external threads.
1.2In the process of locking, the force is uneven or inclined, which maximizes the tilt of the central axis of the screw and nut, and makes the action surface of the screw and the nut thread not fully contacted. The force on the surface is changed to point force or the force on each unit becomes larger.
1.3It can be seen from (fig. 2) that the larger the deflection angle, the smaller the stress area of the thread fit, and the more vulnerable the dental threads are.
1. 4Stainless steel is softer than carbon steel. If iron chips are rubbed off during the locking process, they will adhere to each other and not fall off, thus interfering with the smooth entry and exit of threads, leading to the death of the bottom and top of teeth.
2、Excessive locking force and low thermal conductivity of stainless steel easily lead to thread locking
2.1When locking the nut, the torsion (locking force) must be greater than the friction of the screw and the nut itself before the nut can be rotated. When the nut rotates down along the thread, the screw will stretch because of the reaction force. When the torque (locking force) exceeds the drop point of the screw (safe torque), the residual strain will occur and the screw will remain elongated. When the screw extends beyond its elastic range, it will produce permanent deformation and lead to thread locking.
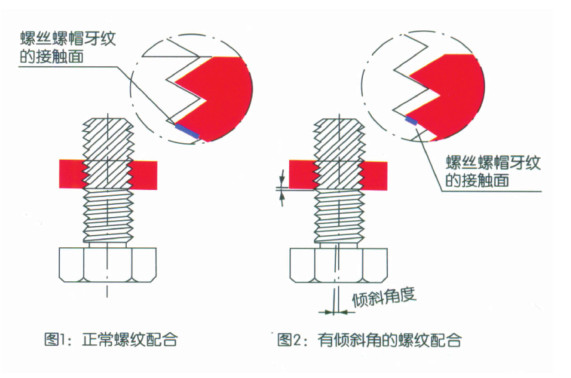
2.2Heat is generated by friction during the rotation of the screw and nut. The thermal conductivity of stainless steel is relatively low (about 1/3 of carbon steel in the range of 10-30w/mc). When the pressure and heat generated destroy the chromium oxide layer (the reason why stainless steel is not easy to rust), the metal dental grain will be blocked/sheared directly, and the stainless steel has a soft characteristic, which leads to adhesion. The greater the locking force, the greater the heat generated, the easier the stainless steel in the screw tooth hill part to produce adhesion. (See Figure 3).
The above principle is the same in the process of loosening (screw and nut, exit). 2. How to Reduce the Lock-in Ratio
In view of the above reasons for easy locking, the use of stainless steel screw should pay attention to as much as possible:
1.Keep the center axis of the screw and nut perpendicular to the locked surface and reduce the deflection angle.
2.Use the torque wrench or sleeve wrench as far as possible to avoid excessive force. Control the torque within the safe stock torque range.
3.Use manual wrench as far as possible to slow down the locking speed, keep the thread clean, use lubricant to reduce friction coefficient, reduce heat energy, thereby reducing adhesion.
4.Select products with relatively high hardness to reduce the shear of threads.
According to the accumulated experience of many experiments and field treatment over the years, our newly developed stainless steel anti-lock agent has obvious effect on reducing the locking ratio. If you need it, please ask for it from our company.
 You only need one phone call to get the best service. If you are looking for the best
You only need one phone call to get the best service. If you are looking for the best
supplier of industrial firmware, please contact us. Immediate consultation
 中文
中文 English
English